National Health Profile 2018
literacy rate is 84.1%. The highest number of rural literates has been recorded in Uttar Pradesh (85.3 million).
Maharashtra (40.1 million) has recorded the highest number of literates in urban areas.
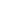
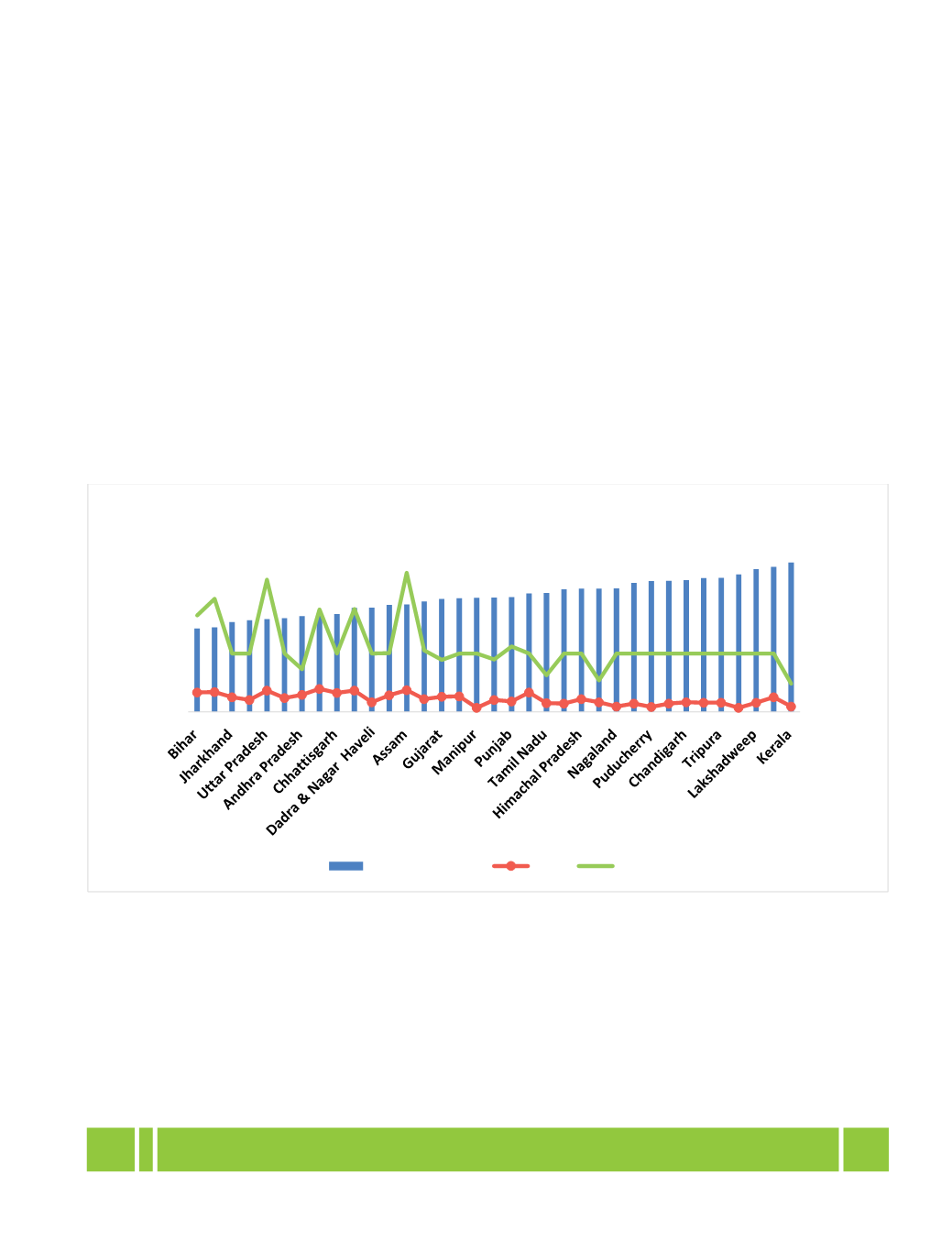
The Maternal Mortality Ratio has shown a decrease of 11 points during 2010-12 to 2011-13. According to the
latest data available maternal mortality ratio is highest for Assam i.e. 300 per 1, 00,000 live births and lowest for
Kerala i.e. 61 per 1, 00,000 live births in 2011-13. Infant mortality rate (IMR) has declined considerably i.e. 37 per
1000 live births in 2015; however, there is a huge gap between IMR of rural (41 per 1000 live births) and urban
(25 per 1000 live births).
There are noteworthy improvements in health indicators such as life expectancy, infant mortality rate (IMR) and
maternal mortality rate (MMR) due to increasing penetration of healthcare services across the country, extensive
health campaigns, sanitation drives, increase in the number of government and private hospitals in India, improved
immunisation, growing literacy etc. Initiatives such as Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakarm, Janani Suraksha Yojana,
Reproductive, Maternal, New-borns, Child and Adolescent Health Services and national programmes to curb
incidences of diseases such as polio, HIV, TB, leprosy etc have played pivotal roles in improving India’s health
indicators. Yet, a huge disparity in the availability of healthcare resources continues to exist in India. The rural-
urban divide is considerable when it comes to healthcare access. Fairly-developed states like Kerala, Maharashtra
and Tamil Nadu have brought down their IMR, TFR and MMR rates and states like Assam, Jharkhand continue to
grapple with these issues even today.
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
0.0
10.0
20.0
30.0
40.0
50.0
60.0
70.0
80.0
90.0
100.0
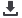
IMR,MMR
Literacy rate
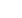
State /UT wise analysis among Literacy rate, IMR and MMR
Female Literacy
IMR
MMR
1800
2500000
Cases and Deaths due to Malaria in India
There are many factors which have an impact on Maternal Mortality Ratio and education level of women is one of
the most important factors in reducing maternal mortality. Education enhances women's ability to access existing
health care resources, including skilled attendants for childbirth, and directly leads to a reduction in her risk of
dying during pregnancy and childbirth.
XIII